Noter
Cliquez ici pour télécharger l'exemple de code complet
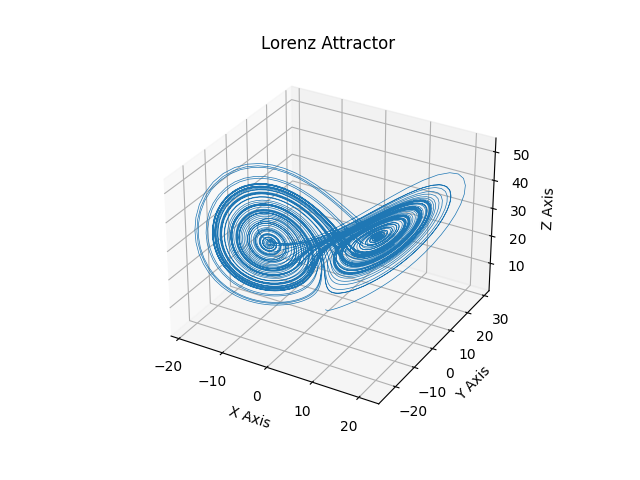
Attracteur de Lorenz #
Ceci est un exemple de tracé du "flux déterministe non périodique" d'Edward Lorenz de 1963 dans un espace tridimensionnel à l'aide de mplot3d.
Noter
Comme il s'agit d'un simple ODE non linéaire, il serait plus facile d'utiliser le solveur ODE de SciPy, mais cette approche ne dépend que de NumPy.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def lorenz(xyz, *, s=10, r=28, b=2.667):
"""
Parameters
----------
xyz : array-like, shape (3,)
Point of interest in three dimensional space.
s, r, b : float
Parameters defining the Lorenz attractor.
Returns
-------
xyz_dot : array, shape (3,)
Values of the Lorenz attractor's partial derivatives at *xyz*.
"""
x, y, z = xyz
x_dot = s*(y - x)
y_dot = r*x - y - x*z
z_dot = x*y - b*z
return np.array([x_dot, y_dot, z_dot])
dt = 0.01
num_steps = 10000
xyzs = np.empty((num_steps + 1, 3)) # Need one more for the initial values
xyzs[0] = (0., 1., 1.05) # Set initial values
# Step through "time", calculating the partial derivatives at the current point
# and using them to estimate the next point
for i in range(num_steps):
xyzs[i + 1] = xyzs[i] + lorenz(xyzs[i]) * dt
# Plot
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(projection='3d')
ax.plot(*xyzs.T, lw=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel("X Axis")
ax.set_ylabel("Y Axis")
ax.set_zlabel("Z Axis")
ax.set_title("Lorenz Attractor")
plt.show()