Noter
Cliquez ici pour télécharger l'exemple de code complet
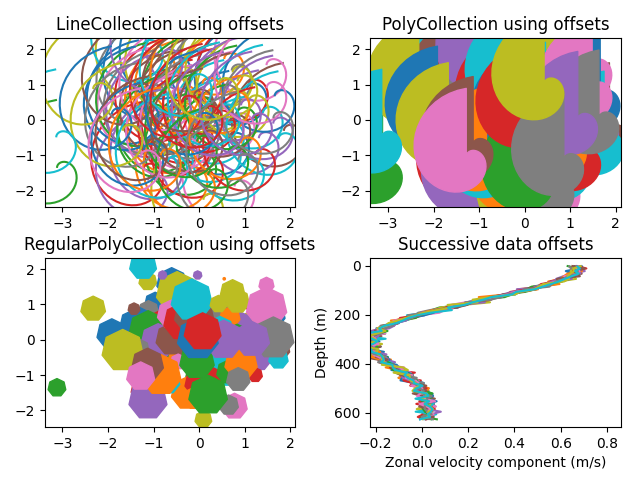
Collection Line, Poly et RegularPoly avec mise à l'échelle automatique #
Pour les deux premières sous-parcelles, nous utiliserons des spirales. Leur taille sera définie en unités de placette, et non en unités de données. Leurs positions seront définies en unités de données à l'aide des arguments de mots- clés offsets et offset_transformLineCollection de
et PolyCollection.
La troisième sous-parcelle fera des polygones réguliers, avec le même type de mise à l'échelle et de positionnement que dans les deux premières.
La dernière sous-parcelle illustre l'utilisation de "offsets=(xo, yo)", c'est-à-dire un seul tuple au lieu d'une liste de tuples, pour générer successivement des courbes de décalage, avec le décalage donné en unités de données. Ce comportement est disponible uniquement pour LineCollection.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import collections, colors, transforms
import numpy as np
nverts = 50
npts = 100
# Make some spirals
r = np.arange(nverts)
theta = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, nverts)
xx = r * np.sin(theta)
yy = r * np.cos(theta)
spiral = np.column_stack([xx, yy])
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
rs = np.random.RandomState(19680801)
# Make some offsets
xyo = rs.randn(npts, 2)
# Make a list of colors cycling through the default series.
colors = [colors.to_rgba(c)
for c in plt.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'].by_key()['color']]
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2)
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.92, left=0.07, right=0.97,
hspace=0.3, wspace=0.3)
col = collections.LineCollection(
[spiral], offsets=xyo, offset_transform=ax1.transData)
trans = fig.dpi_scale_trans + transforms.Affine2D().scale(1.0/72.0)
col.set_transform(trans) # the points to pixels transform
# Note: the first argument to the collection initializer
# must be a list of sequences of (x, y) tuples; we have only
# one sequence, but we still have to put it in a list.
ax1.add_collection(col, autolim=True)
# autolim=True enables autoscaling. For collections with
# offsets like this, it is neither efficient nor accurate,
# but it is good enough to generate a plot that you can use
# as a starting point. If you know beforehand the range of
# x and y that you want to show, it is better to set them
# explicitly, leave out the *autolim* keyword argument (or set it to False),
# and omit the 'ax1.autoscale_view()' call below.
# Make a transform for the line segments such that their size is
# given in points:
col.set_color(colors)
ax1.autoscale_view() # See comment above, after ax1.add_collection.
ax1.set_title('LineCollection using offsets')
# The same data as above, but fill the curves.
col = collections.PolyCollection(
[spiral], offsets=xyo, offset_transform=ax2.transData)
trans = transforms.Affine2D().scale(fig.dpi/72.0)
col.set_transform(trans) # the points to pixels transform
ax2.add_collection(col, autolim=True)
col.set_color(colors)
ax2.autoscale_view()
ax2.set_title('PolyCollection using offsets')
# 7-sided regular polygons
col = collections.RegularPolyCollection(
7, sizes=np.abs(xx) * 10.0, offsets=xyo, offset_transform=ax3.transData)
trans = transforms.Affine2D().scale(fig.dpi / 72.0)
col.set_transform(trans) # the points to pixels transform
ax3.add_collection(col, autolim=True)
col.set_color(colors)
ax3.autoscale_view()
ax3.set_title('RegularPolyCollection using offsets')
# Simulate a series of ocean current profiles, successively
# offset by 0.1 m/s so that they form what is sometimes called
# a "waterfall" plot or a "stagger" plot.
nverts = 60
ncurves = 20
offs = (0.1, 0.0)
yy = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, nverts)
ym = np.max(yy)
xx = (0.2 + (ym - yy) / ym) ** 2 * np.cos(yy - 0.4) * 0.5
segs = []
for i in range(ncurves):
xxx = xx + 0.02*rs.randn(nverts)
curve = np.column_stack([xxx, yy * 100])
segs.append(curve)
col = collections.LineCollection(segs, offsets=offs)
ax4.add_collection(col, autolim=True)
col.set_color(colors)
ax4.autoscale_view()
ax4.set_title('Successive data offsets')
ax4.set_xlabel('Zonal velocity component (m/s)')
ax4.set_ylabel('Depth (m)')
# Reverse the y-axis so depth increases downward
ax4.set_ylim(ax4.get_ylim()[::-1])
plt.show()
Références
L'utilisation des fonctions, méthodes, classes et modules suivants est illustrée dans cet exemple :