Noter
Cliquez ici pour télécharger l'exemple de code complet
Voxel 3D / tracé volumétrique avec couleurs RVB #
Démontre l'utilisation Axes3D.voxelspour visualiser des parties d'un espace colorimétrique.
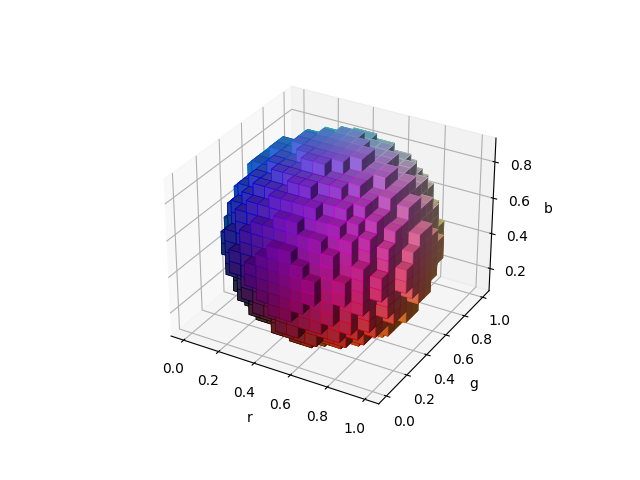
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def midpoints(x):
sl = ()
for i in range(x.ndim):
x = (x[sl + np.index_exp[:-1]] + x[sl + np.index_exp[1:]]) / 2.0
sl += np.index_exp[:]
return x
# prepare some coordinates, and attach rgb values to each
r, g, b = np.indices((17, 17, 17)) / 16.0
rc = midpoints(r)
gc = midpoints(g)
bc = midpoints(b)
# define a sphere about [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
sphere = (rc - 0.5)**2 + (gc - 0.5)**2 + (bc - 0.5)**2 < 0.5**2
# combine the color components
colors = np.zeros(sphere.shape + (3,))
colors[..., 0] = rc
colors[..., 1] = gc
colors[..., 2] = bc
# and plot everything
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(projection='3d')
ax.voxels(r, g, b, sphere,
facecolors=colors,
edgecolors=np.clip(2*colors - 0.5, 0, 1), # brighter
linewidth=0.5)
ax.set(xlabel='r', ylabel='g', zlabel='b')
ax.set_aspect('equal')
plt.show()
Durée totale d'exécution du script : (0 minutes 1,625 secondes)