Noter
Cliquez ici pour télécharger l'exemple de code complet
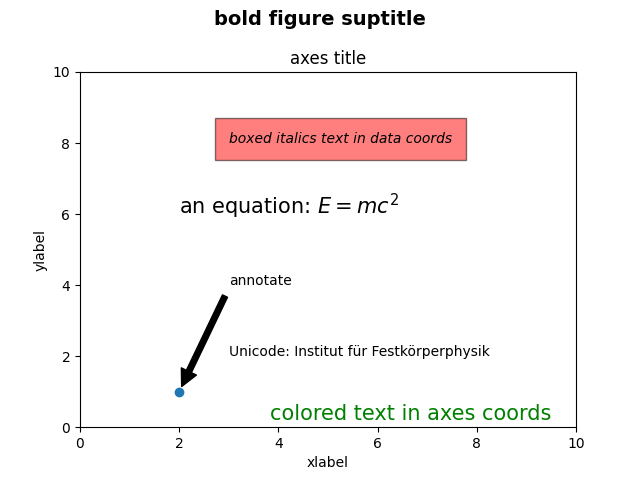
Commandes de texte #
Traçage de texte de nombreux types différents.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('bold figure suptitle', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax = fig.add_subplot()
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.85)
ax.set_title('axes title')
ax.set_xlabel('xlabel')
ax.set_ylabel('ylabel')
ax.text(3, 8, 'boxed italics text in data coords', style='italic',
bbox={'facecolor': 'red', 'alpha': 0.5, 'pad': 10})
ax.text(2, 6, r'an equation: $E=mc^2$', fontsize=15)
ax.text(3, 2, 'Unicode: Institut f\374r Festk\366rperphysik')
ax.text(0.95, 0.01, 'colored text in axes coords',
verticalalignment='bottom', horizontalalignment='right',
transform=ax.transAxes,
color='green', fontsize=15)
ax.plot([2], [1], 'o')
ax.annotate('annotate', xy=(2, 1), xytext=(3, 4),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05))
ax.set(xlim=(0, 10), ylim=(0, 10))
plt.show()
Références
L'utilisation des fonctions, méthodes, classes et modules suivants est illustrée dans cet exemple :